Blocked artery image
What causes inflammation in the arteries? and what is the connection between Inflammation and Heart Disease. Heart disease is caused by a condition called atherosclerosis, it is a very serious disease characterized by chronic inflammation and fibrotic deterioration in the innermost layer of the medium and large arteries.
Basically, what happens is, when an injury occurs in the vascular wall the body produces inflammation in response to this attack, the major risk factors for developing cardiovascular disease (hypertension, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol) are the primary cause of this injury.
Over 20 years ago clinical research discovered that elevated levels of artery inflammation was a significant factor in heart disease and stroke. At the time it wasn’t known if an anti-inflammatory treatment could prevent the occurrence of inflammation in the arteries.

Scientific studies
Study of inflammation
Back in 2008 a large study of 17,802 people took 1.9 months to conclude and in which the participants were given (LDL) low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels of less than 130 milligrams per deciliter (3.4 mmol per liter) and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels of 2.0 milligrams per liter or higher to (a statin drug) rosuvastatin, 20 milligrams each day found that the older participants who had normal cholesterol had markers for artery inflammation.
At the time it was known that statin drugs lowered cholesterol but it wasn’t known that they could reduce inflammation in the arteries as well.
A further study published in 2011 by Clinical trials. Gov known as Cantos stated that by injecting an anti-inflammatory drug into people who had suffered a heart attack who also had markers for inflammation in the arteries could have a significant effect on inflammation in the arteries.
During this study it was found that by treating people with this unusual anti-inflammatory treatment could reduce the instance of a heart attack or strokes by as much as 15%. Furthermore it also reduced the number of interventions such as bypass surgery and angioplasty by 30%.
Basically what these two studies are saying is by controlling inflammation in the arteries you have a significant impact on the number of heart attacks and strokes cases.
What is inflammation in the arteries?
To put the word inflammation into simple terms, it occurs when our bodies have suffered some type of trauma or infection for example a swollen joint that is usually red in colour, another example would be if you smashed your leg against a hard object and a bruise occurred because of the impact.
Our bodies are primed to respond to events like this by releasing chemicals to fight against infection it also releases white blood immune cells that help to heal the affected area. Similarly when damage is caused to the blood vessels it answers the question what causes inflammation in the arteries.
Long term inflammation
Were you aware that inflammation can be a long term health issue? Inflammation can be a “slow burner” in response to sometimes weight issues, not enough physical activity or elevated levels of blood sugars (glucose) these issues can in their own way cause inflammation so our bodies respond.
Cardiovascular disease
It has yet to be proven that inflammation has a direct impact in causing cardiovascular disease although we do know that chronic low grade inflammation is linked to atherosclerosis in all of it’s stages, atherosclerosis is an underlying disease that associated with heart attacks, stroke and PAD (peripheral artery disease)
 Atherosclerosis
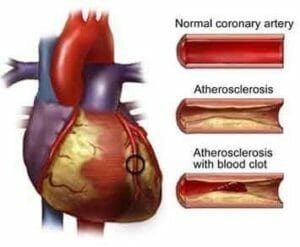
Atherosclerosis
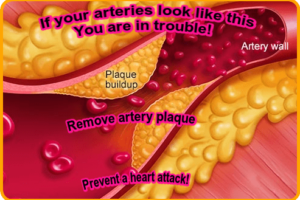
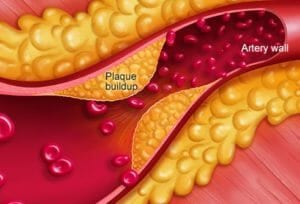
Atherosclerosis is a hardening of the arteries, it is layers of cholesterol, calcium and debris otherwise known as plaque, over time it gathers and deposits along the inside of the blood arteries or blood vessels, this is very common as we get into our late thirties and onwards.
Coronary heart disease
Coronary heart disease occurs when atherosclerosis is present in the blood vessels that bring oxygen rich blood to the heart muscle, atherosclerosis in the blood vessels that supply blood to the brain, the legs, the arms and the gut can also have an impact on blood flow.
Damage to the arteries
LDL or low density lipoprotein is commonly known as “bad” cholesterol is the trigger for heart disease and stroke although it isn’t quite clear what causes this. It is thought that when white blood cells link with LDL plaque formation occurs, plaque is made up of cholesterol, fatty materials, calcium and dead cells, the gradual formation of plaque build up increases what causes inflammation in the arteries resulting in continuous damage the arteries.
How long does plaque build up take?
Studies have shown the atherosclerotic plaque build up can take decades, it is important to know that it can start in your childhood in a small way but over the years plaque will increase and grow in size, think about it in terms of a waste water pipe in your house that has silt in it, over time it will start to block much like an artery.
The outcome is a reduction of blood flow to the major organs including the heart, a symptom of a blockage could be angina, plaque comes in two forms stable and unstable, unstable plaque can break off and cause a heart attack or a stroke.
Plaque rupture
Plaque in the arteries has a covering called a fibrous cap, it is thought that initially the cap becomes damaged because of erosion or a rupture, when this happens a layer of cells releases a chemical component into the bloodstream causing an overaction in the body.
This triggers a blood clot inside the arteries causing a blockage of blood going to the heart damaging the heart muscle, while this process isn’t fully understood it is hypothesized that chronic inflammation within arterial walls plays a major role making unstable plaque more likely to rupture
The risks of inflammation
Inflammation is a common denominator in heart disease and stroke patients, inflammation is thought to be a signal of the promotion of fatty deposits in the arterial system.
Though we have no proof that it causes cardiovascular disease it is rather important that we understand inflammation and its role in a healthy or unhealthy heart.
 Risk factors for heart disease
Risk factors for heart disease
The main risk factors for heart disease are high blood pressure, cigarette smoking and bad cholesterol (LDL) these risks can cause injury to the heart.
Following an injury to the arterial wall atherosclerosis or the accumulation of fatty deposits that stick to the inner wall of the arteries start to develop.
Arterial plaque
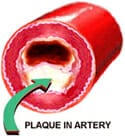
Narrowing of the arteries
This build up leads to a narrowing of the arteries increasing the risk of a major blockage in the form of a heart attack or stroke.
We still need more research on how inflammation influences heart attacks and stroke, but it would seem that inflammation is the instigating event in many heart attacks and certain forms of stroke in fatty build-up and ldl cholesterol rich plaque in blood vessels.
From the research we know that inflammation plays a leading role when atherosclerosis becomes more advanced, lesions that form during this phase usually have no clinical symptoms until they regress and rupture. This process begins when extracellular lipids accumulate killing the cells in the centre of the plaque.

fatty deposits
Plaque build-up
Our bodies react to plaque build-up by trying to keep it away from the flow of blood, it sees the plaque as not normal and foreign or not belonging in the healthy blood vessels.
This reaction is bringing inherent danger because the plaque may rupture if it comes away from the arterial wall and forms a dangerous clot.
Most heart attacks and certain types stroke are mainly caused by the combination of formation of plaque and blood clots. If the blood flow to the artery leading to the heart is obstructed, it may cause a heart attack and if the blood flow to the brain is obstructed it may cause an ischemic stroke.
Lowering your risk is crucial
For many years statins medications have been used to lower cholesterol, it is debatable whether the statins reduce inflammation or is it because of lowering cholesterol, the jury is still out on that one.
There are several ongoing clinical trials testing other medications on lowering cholesterol in the arterial system to reduce the risks of a heart attack or stroke.
Conclusion
To summarize this article about what causes inflammation in the arteries, inflammation does have a part to play during the whole atherosclerosis disease process, vascular lipid build-up is the main reason or cause of this inflammation.
To limit the main risk factors and high cholesterol must be uppermost in people’s minds, we still await better treatment of the inflammation process which generally happens in response to damage to the endothelial wall of the artery.
A New Treatment
A new natural treatment from Pure encapsulations called L-Arginine 700 mg has shown promise in the approach to cardiovascular disease is the use of amino acid L-Arginine to help with the repair of the inflamed blood vessels, lower blood pressure and remove plaque build-up.
The best known of these supplemental food products is Pure Encapsulations L-Arginine 700 mg containing L-Arginine with L-Citrulline in the formula, People have used Pure Encapsulations L-Arginine 700 mg and the reports and feedback have been good.
The combination of the award winning Doctor’s Best L-Arginine and the L-arginine based Nitric Oxide Ultra seems to reduce inflammation in the arteries, lower bad cholesterol, increase good cholesterol and get rid of plaque build-up.
Why not give them a try? Go to Herbs Direct for more details.
References:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3822968/
http://med.stanford.edu/news/all-news/2012/12/international-study-points-to-inflammation-as-cause-of-plaque-buildup-in-heart-vessels-researchers-say.html
https://bjsm.bmj.com/content/51/15/1111
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartjsupp/article-pdf/4/suppl_A/A18/9795962/A18.pdf